Very few chemicals affect human life in as many ways as sulfuric acid. It is used to produce thousands of everyday consumer products and is considered one of the most important industrial chemicals.
What is sulfuric acid?
Sulfuric acid (also called sulfuric acid or hydrogen sulfate) is a dense, colorless liquid with the chemical formula H2SO4, molar mass 98.079 g/mol, molecular density 1.84 kg/L (compared to water 1 kg/L), and boiling point 337°C. H2SO4 has an oil-like viscosity, especially in concentrated form, and appears like a clear, heavy syrup. Because of its greasy appearance, it was once called vitriol oil (now only used for concentrated commercial forms). However, unlike ordinary oils, sulfuric acid is a strong acid with high corrosive properties.
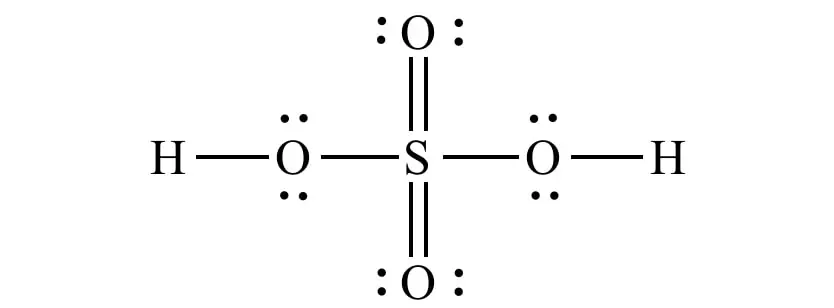
Structural formula of H2SO4. Image: Internet.
In its purest form, H2SO4 solution is a highly corrosive liquid with a pH of 0.5 and can be diluted with water at any concentration. Prolonged exposure to low concentrations or short-term exposure to high concentrations can harm health. Concentrated sulfuric acid is very dangerous, causing skin burns and severe tissue damage upon contact.
Why is H2SO4 highly corrosive?
Two main properties explain the high corrosiveness of sulfuric acid:
- First, it is a very strong dehydrating agent, strongly combining with water. Specifically, when H2SO4 comes into contact with any solid containing water or moist air, it quickly absorbs water molecules and dries the material. Because this process can be quite vigorous, it can cause a combustion-like reaction with many organic materials such as wood, paper, or sugar, leaving carbon residue.
Due to this property with water, pure concentrated sulfuric acid does not exist naturally. Although volcanic activity can produce hydrogen sulfate and sulfuric acid aerosols from eruptions that may persist in the stratosphere for years, these aerosols can later convert into SO2, a component of acid rain.
- The second property of sulfuric acid is its tendency to ionize easily. In dilute sulfuric acid solution, hydrogen and sulfate (SO42-) ions separate, forming many hydronium ions and free negatively charged sulfate ions capable of binding to other atoms. As a result, H2SO4 readily reacts with many metals, carbon, sulfur, and other substances.
How is H2SO4 produced?
Sulfuric acid is produced from sulfur. First, sulfur dioxide (SO2) is obtained by burning molten sulfur. Then, in the presence of a vanadium pentoxide catalyst, SO2 is converted into sulfur trioxide (SO3).

The process for producing H2SO4 is as follows:
Step 1: Prepare sulfur dioxide
S(s) + O2(g) → SO2 (g)
Step 2: Prepare sulfur trioxide
Sulfur trioxide is formed when sulfur dioxide reacts with oxygen in a 1:1 ratio at 400–450°C and 1–2 atm in the presence of a V2O5 (vanadium oxide) catalyst. This reaction is reversible, occurring in both directions under the same conditions.
2SO2(g) + O2(g) ⇌ 2SO3(g)
Step 3: Prepare concentrated sulfuric acid
The initially formed sulfur trioxide is made to react with sulfuric acid solution. Sulfur trioxide cannot dissolve directly in water because it forms a mist. The product of this reaction is H2S2O7, also called oleum, disulfuric acid, or pyrosulfuric acid (a sulfur oxoacid). Finally, the obtained oleum is dissolved in water to produce concentrated sulfuric acid.
H2SO4 + SO3(g) → H2S2O7(l)
H2S2O7(l) + H2O(l) → 2H2SO4
How to safely dilute concentrated H2SO4
Diluting sulfuric acid is a common procedure in laboratories and industrial production. Depending on the application, the concentration of this strong oxidizing compound can vary. Water is usually used to dilute concentrated H2SO4. However, this process can be risky if not done correctly. Understanding and following the correct procedure ensures safety, maintains solution quality, and guarantees effectiveness in practical use.
As mentioned, H2SO4 is highly corrosive and reacts violently with water, releasing significant heat, especially in concentrated form. Therefore, dilution must be controlled to ensure absolute safety for both the operator and the environment. Personal protective equipment such as safety goggles, chemical-resistant gloves, lab coats, and, if necessary, gas masks should be worn. Use glass or acid-resistant equipment, and perform dilution in a fume hood or well-ventilated area with emergency handling systems.
The most important rule is: always add acid to water and never the reverse. Why?
- When concentrated sulfuric acid is slowly added to water, the heavier acid sinks, and the released heat is dissipated in the water, minimizing the risk of localized boiling and splashing. Sudden contact of water with acid generates steam due to the heat of the reaction.
- Conversely, water is much lighter than sulfuric acid. If water is poured into acid, it floats on top, leaving only a small contact area. When water and acid meet, the reaction is immediate, causing violent boiling, steam, and splashing, which can eject the solution from the container.

Always add concentrated H2SO4 to water when diluting to ensure safety. Image: Internet
The proper steps for safely diluting concentrated H2SO4 solution are as follows:
1. Protective equipment: Wear safety goggles, gloves, gas mask, lab coat, etc. Also, prepare emergency measures such as safety shower, wash basin, and acid neutralizing chemicals (e.g., sodium bicarbonate).
2. Equipment: Use heat-resistant glassware or specialized plastic containers that are resistant to strong inorganic acids. Prepare a glass rod or magnetic stirrer with heating capability.
3. Dilution process: Pour distilled water into the container first. Then, slowly add concentrated H2SO4 to the water in small portions, stirring constantly to disperse heat. Never stop stirring while adding acid. Add gradually to prevent local overheating, thermal shock, container cracking, or violent reaction. Keep the container stable and ensure good ventilation throughout the process.
4. Cooling and storage: After dilution, allow the solution to cool completely before use or storage. Label the container clearly with concentration, date, preparer, and necessary safety warnings. Handling and storage must follow regulations for hazardous chemicals.
What is H2SO4 used for?
Thanks to its strong chemical properties, such as high acidity, water absorption, and strong oxidizing ability, H2SO4 can be applied in households, but it is mainly widely used in various industries and is considered one of the most important industrial chemicals.
Household cleaning:
Due to its relatively high hazards, H2SO4 is not recommended for general household cleaning. However, in special cases, this highly corrosive chemical is mainly used in grease cleaners and drain cleaners (to corrode and quickly decompose organic waste causing clogs, making drain unclogging easier), but only in strictly controlled concentrations and with clear warnings. It is a very dangerous chemical that must be handled carefully.
Precautions when using sulfuric acid to unclog drains at home:
-
Read the instructions carefully before use.
-
Always wear appropriate protective equipment, including gloves, goggles, and a gas mask to protect yourself from splashes or fumes.
-
Ventilation: Ensure the room or area is well-ventilated. Open windows or use an exhaust fan to reduce toxic fumes during drain cleaning.
-
Never mix products containing H2SO4 with any other chemicals or cleaners, as this can cause dangerous chemical reactions that release toxic gases and pose fire and explosion risks.
-
First aid: If acid splashes on your skin, rinse the affected area with plenty of water and seek medical attention immediately.
-
Store in a cool, well-ventilated place, away from children, pets, and flammable materials. If H2SO4 spills or the container leaks, clean up the chemical properly to prevent it from spreading.
Industrial applications of H2SO4
1. Chemical production
Sulfuric acid is one of the most important base chemicals in the chemical industry. With its characteristic chemical properties, it participates directly or indirectly in many processes for producing basic chemicals, serving as a reactant, intermediate, and catalyst in large-scale synthesis chains. For example, it is used as an intermediate to produce other useful acids such as nitric acid (by reacting with nitrate salts like KNO3, NaNO3) and hydrochloric acid (by reacting with sodium chloride). It can also be used to produce synthetic cleaners, pigments and dyes, as well as sulfate salts.
2. Metal processing
Sulfuric acid is widely used in metal processing. Metalworking involves heating, cooling, and shaping metals to create products made from steel, iron, or copper (e.g., vehicles, computer components, construction, pipelines, housing materials, etc.).
Sulfuric acid is used in a mixture called “pickling,” a surface treatment process used to remove rust or carbon impurities to finish the metal, which is one of the final and most important stages of metal treatment. It is also used to clean metals before plating.
3. Battery production
This chemical (CAS 7664-93-9) is combined with lead to produce a reaction that generates enough electrons to produce the voltage needed for large batteries, such as those used in cars and tractors. Therefore, it is sometimes called “battery acid” and is essential for generating energy in batteries.
4. Household and industrial cleaning products
Due to its extremely corrosive nature, sulfuric acid is a main ingredient in many cleaning products and drain cleaners. It is also used to produce sulfate salts, explosives, rubber and plastics, dyes, paper, textiles, paints, fire extinguishers, and disinfectants.
5. Pharmaceutical production
-
Sulfuric acid is used to destroy cancer cell DNA in chemotherapy drug production.
-
It is involved in the manufacture of sedatives (Diazepam/Valium), painkillers, fever reducers, and anti-inflammatory drugs (Aspirin, Paracetamol), antibiotics (Chloramphenicol), anti-inflammatory drugs (Prednisolone), antibacterial drugs (Sulfanilamide), and synthetic corticosteroids.
-
It is also a key component of Debacterol ointment for treating various skin infections and oral ulcers.
6. Food processing
Why is a toxic acid used in food? Sulfites and sulfur dioxide help prevent food spoilage and formation of harmful substances like nitrosamines. This strong inorganic acid is used to break down cell walls of fruits and vegetables for easier digestion or to preserve food by killing bacteria and fungi before they grow.
7. Petroleum and fuel production
Although not directly involved in hydrocarbon cracking, sulfuric acid is indirectly used in post-cracking processes to create more manageable compounds before refining into gasoline and gas. Specifically, it is mainly used in alkylation, acting as a catalyst to produce alkylate, a high-octane gasoline component for cleaner, lead-free fuel. It is also used in oil treatment to remove unstable organic impurities like resins and nitrogen compounds, improving the color and stability of gasoline, diesel, and lubricants. Sulfuric acid also participates in producing sulfonic surfactants, additives for fuels and lubricants.
8. Waste management
Many industrial wastes are dumped in landfills. Sulfuric acid is used to neutralize organic matter and prevent the release of toxic gases. It also acts as a catalyst to break chemical bonds in materials. The EPA sets limits on sulfuric acid discharge, but it remains hazardous to humans.
9. Agricultural applications
The largest use of sulfuric acid in agriculture is fertilizer production. Phosphoric acid is extracted from phosphate rock and treated with hydrogen sulfate to produce inorganic phosphate fertilizers such as ammonium sulfate and superphosphate. These fertilizers are applied to fields to supply nutrients for crops.
Where to buy reliable H2SO4 in Vietnam?
If you want to purchase high-quality sulfuric acid at a reasonable price for production processes, laboratories, schools, etc., KPTCHEM is an excellent supplier for you. As one of the leading H2SO4 suppliers in Vietnam, KPTCHEM has a highly skilled team and a fleet of specialized tank trucks to deliver quality products at optimal cost. We not only deliver domestically but can also ship internationally while ensuring the best chemical quality. Contact our consulting team for fast 24/7 support.
FAQ
Uses of concentrated sulfuric acid in sugar mills?
In sugarcane processing, raw cane juice contains impurities such as soil, organic matter, microorganisms, colorants, and mineral salts. To clarify the juice and improve sugar crystallization, mills adjust the pH by using diluted concentrated sulfuric acid to lower the juice pH to the optimal level, helping impurities precipitate and be removed. In sulfitation processes, a slightly acidic environment allows SO2 to react better, producing a bright and stable sugar color.
In ion exchange systems, sulfuric acid is used to regenerate cation resins when their ion-exchange capacity is depleted. Additionally, after lime treatment, the juice may become too alkaline, and H2SO4 is used to neutralize the excess alkali, ensuring safety and meeting environmental standards.
What color does H2SO4 turn litmus paper?
Answer: Red. Sulfuric acid is a strong acid, dissociating completely into hydrogen ions (H+) and sulfate ions (SO42-). The H+ ions react with litmus paper, turning it red.
Which metals react with dilute H2SO4?
Like other acids, dilute sulfuric acid reacts with metals to produce hydrogen gas and metal sulfates. Metals that react include iron (Fe), aluminum (Al), zinc (Zn), manganese (Mn), and magnesium (Mg).
Dilute H2SO4 does not react with copper (Cu), silver (Ag), or gold (Au).
Why does sucrose turn black in concentrated H2SO4?
Sulfuric acid is a strong acid and a dehydrating agent. It adds a proton (H+) to water, forming hydronium ions (H3O+), which remove water. With carbohydrates (sugar, glucose, starch, cellulose, etc.), sulfuric acid removes hydroxyl groups (-OH) from carbon atoms.
Sucrose (C12H22O11), like other carbohydrates, undergoes acetal bond breakdown. The reaction produces carbon and water, releasing enough heat to generate black steam:
C12H22O11 → 12C + 11H2O
It acts similarly on starch, cellulose, and even human tissue. That is why using concentrated sulfuric acid is extremely dangerous, requiring protective equipment during handling, production, or experiments.



